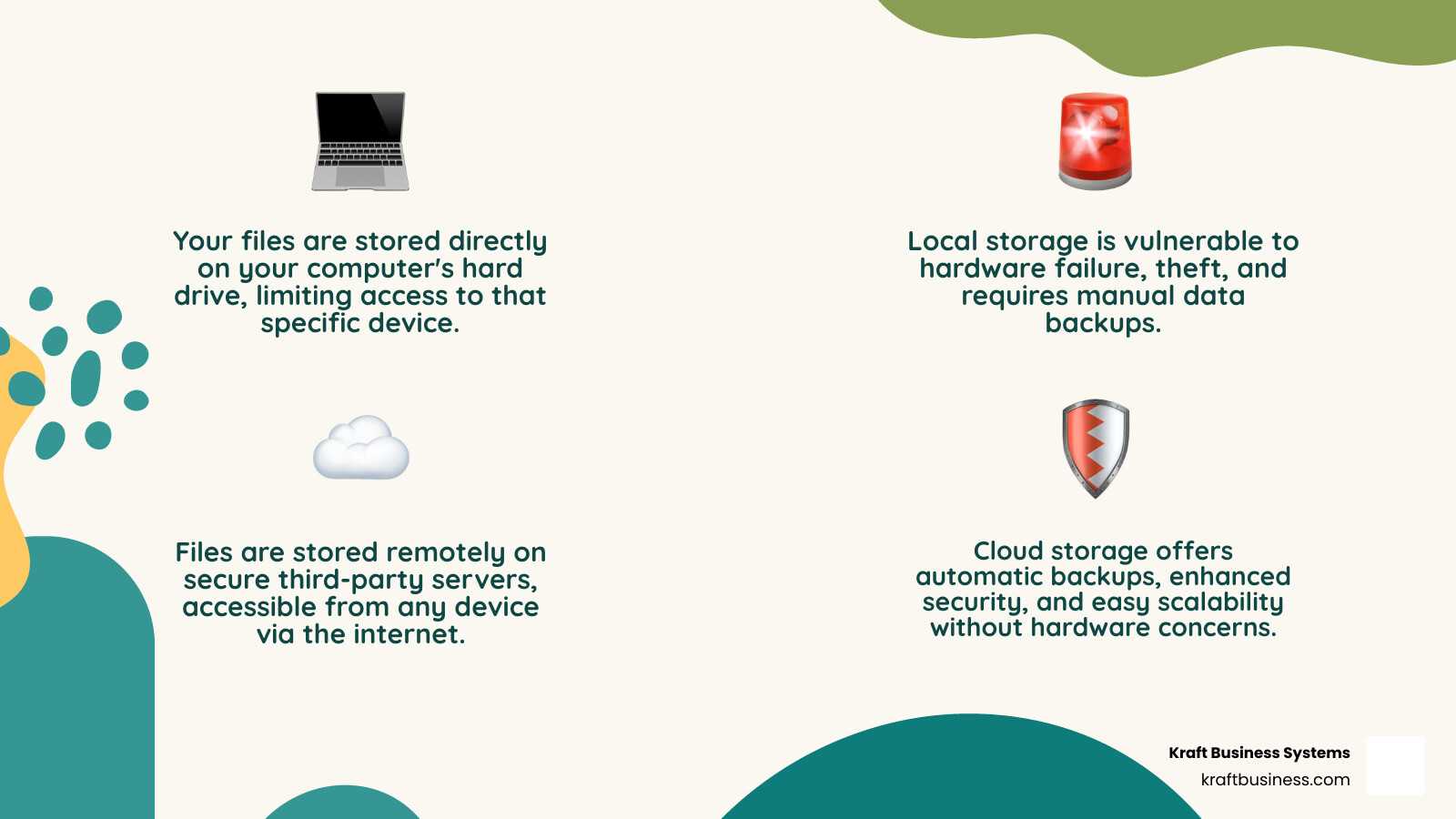
Cloud based data storage is a model where digital files are stored on remote servers owned by third-party providers, accessible via the internet instead of a local hard drive.
Quick Answer for Cloud Based Data Storage:
- What it is: Remote data storage on third-party servers accessed via internet
- How it works: Upload files to provider’s data centers, access from any device online
- Key benefits: Cost savings, scalability, automatic backups, global accessibility
- Main types: Public, private, hybrid, and multicloud deployments
- Storage formats: Object storage (unstructured data), file storage (folders/files), block storage (databases)
- Security: Shared responsibility between provider and user, with encryption and access controls
Instead of keeping documents in an office filing cabinet, you store them in a secure, professionally managed facility accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
The global cloud storage market, valued at $108.69 billion in 2023, is projected to hit $665 billion by 2032, growing 22.4% annually. This reflects a rapid shift from traditional storage, which required buying and maintaining physical hardware.
With cloud storage, you pay only for what you use, and the provider handles the technical complexities. This is especially useful since 90% of organizational data is unstructured (emails, videos, documents), which cloud systems manage efficiently.
Essential cloud based data storage terms:
Cloud Based Data Storage Explained: Definition & Key Concepts
How It Works and the Powerful Advantages
Think of cloud based data storage as having experts manage your documents in a secure, accessible library. Instead of using office filing cabinets, you entrust files to professionals who specialize in keeping information safe.
When you save a file to the cloud, it travels via the internet to massive data centers. Your data is spread across multiple servers and locations through virtualization. Third-party providers manage all the hardware, software, and security, so you connect seamlessly through an app or API.
The system’s primary advantages are clear:
- Scalability: Instantly get more or less storage space as your needs change. Unlike traditional storage, you don’t have to guess future needs and buy expensive equipment upfront.
- Cost-effectiveness: Shift from large capital expenditures on hardware to predictable monthly operational costs. You pay only for what you use.
- Accessibility: Your team can access files from anywhere, whether at our Grand Rapids office or visiting a client in Detroit, breaking down geographical barriers.
- Business continuity: Your data remains safe in professionally managed data centers during local disasters or equipment failures, ensuring your business keeps running.
These advantages explain why cloud computing delivers such powerful benefits for businesses of all sizes.
Key benefits of cloud based data storage
Beyond the fundamentals, cloud based data storage offers specific operational benefits that can transform your business:
- Increased agility: Respond to opportunities faster by provisioning storage for new projects in minutes, not weeks.
- Faster deployment: Accelerate software testing and application launches, as your IT team spends less time on infrastructure setup.
- Global access and collaboration: Allow team members to edit documents simultaneously and stay synchronized, regardless of their location.
- Reduced IT workload: Free your technical staff from routine maintenance to focus on strategic initiatives that drive growth.
- Improved collaboration: With files in the cloud, version control is automatic and sharing is secure, integrating remote team members.
- Efficiently handle unstructured data: Seamlessly store emails, videos, and documents, providing a foundation for advanced analytics.
These benefits work together to create a more agile, efficient organization. Learn how cloud computing can revolutionize your business operations and open up new possibilities for growth.
The role of data backup and disaster recovery
Cloud based data storage serves as your business’s insurance policy against data loss.
- Off-site location advantage: Your data remains secure in geographically distant data centers during local disasters, ensuring business continuity.
- Automation: Scheduled backups run automatically, eliminating human error and reducing the risk of data loss.
- Redundancy: Data is copied across multiple servers and locations, with some providers achieving 99.999999999% durability.
- Data protection: Features like versioning help you restore files to a state before a ransomware attack. Immutable storage options can create an unalterable recovery foundation.
- Faster recovery: Get your business operational in hours instead of days or weeks after a data loss event.
The combination of these features creates a robust safety net that traditional backup methods simply cannot match. Find the powerful benefits of cloud data protection and how they can safeguard your business’s future.
Understanding the Core of Cloud Based Data Storage Models
Choosing a cloud based data storage model is like picking the right tool for the job. The cloud’s flexibility can serve a small shop in Benzonia as effectively as a large enterprise in Warren.
Behind the scenes, sophisticated data architecture presents your files as a single, scalable resource. This ensures your data is accessible and durable without you needing to manage the hardware. Learn about the four main types of cloud computing that make these models possible.
The three main types of storage
Cloud based data storage offers three distinct approaches for different needs.
File storage organizes data in a familiar hierarchy of files and folders, making it intuitive for team collaboration and shared drives.
Block storage breaks data into uniform chunks, or blocks, for high-speed access. This makes it ideal for databases and performance-intensive applications.
Object storage is designed for massive amounts of unstructured data like emails, videos, and documents. Each item is an “object” with its data and metadata, which is critical since 90% of organizational data is unstructured. This research on unstructured data highlights its importance.
| Type of Storage | Structure & How It Works | Best For | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| File Storage | Organized in a hierarchical structure of files and folders, similar to a traditional computer hard drive. Data is accessed via common protocols like SMB or NFS. | General-purpose files, shared drives, applications that need a file system. | Team collaboration, file sharing, user home directories, large content repositories, development environments. |
| Block Storage | Data is broken into fixed-size blocks, each with a unique identifier, and stored as separate pieces. These blocks don’t contain metadata, requiring a separate database to manage their relationship. Offers very low latency. | High-performance applications, databases, virtual machines, workloads requiring fast, direct access. | Transactional databases (e.g., SQL, NoSQL), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), high-performance computing (HPC). |
| Object Storage | Data is stored as “objects” in flat data pools, each bundled with its metadata (information about the object, like creation date, author, or content type) and a unique identifier. This makes it ideal for unstructured data. | Unstructured data, massive scale, long-term retention, cloud-native applications. | Data archiving, data lakes for analytics and AI/ML, content delivery networks (CDNs), backup and disaster recovery, media libraries (photos, videos), web content. |
Public, private, hybrid, and multicloud deployment
Deploying your cloud based data storage involves choosing between four main models based on your needs for control, cost, and flexibility.
Public cloud storage is owned by a third-party provider and shared among tenants. It offers excellent scalability and cost-effectiveness but less direct control.
Private cloud storage is dedicated exclusively to your organization. It provides maximum control and security for compliance but requires a higher investment.
Hybrid cloud storage combines public and private clouds, allowing you to balance security, cost, and scalability. This model adds management complexity.
Multicloud strategies use services from multiple providers to avoid vendor lock-in and access best-of-breed features, though this can increase complexity and cost.
The right model depends on your business needs, security requirements, and budget. We help clients design a strategy that aligns with their goals. Find how hybrid cloud security solutions can benefit your business.
Key Considerations for Your Cloud Strategy
Adopting cloud based data storage requires a solid plan. Just as you would carefully consider a new home, you must evaluate your cloud options to fit your business needs.
Key elements of a successful cloud strategy include careful vendor selection, understanding the guarantees in Service Level Agreements (SLAs), and planning for data migration to avoid downtime or data loss.
A cookie-cutter approach rarely works. Your strategy must align with your specific business goals, security requirements, and budget. Understanding cloud adoption strategies can make this process much smoother.
Security and compliance in the cloud
When you move to the cloud, security is a shared responsibility. The provider secures the infrastructure (data centers, servers, networks), but you are responsible for securing your data within it.
This means implementing encryption for data both in transit (traveling over the internet) and at rest (stored on servers). It also requires strong access controls to ensure employees can only access the data necessary for their jobs.
For businesses handling sensitive information, regulatory compliance (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) is critical. Major cloud providers invest heavily in certifications, often exceeding what a business could achieve alone, but you must still configure services correctly.
We help Michigan businesses steer these security challenges. Learn more about our approach to cloud security and how we help manage data access controls.
Cost implications and pricing models
One of the biggest advantages of cloud based data storage is paying only for what you use. However, it’s important to understand the pricing models.
The pay-as-you-go model is affected by more than just storage capacity. Data transfer costs, especially egress fees for downloading data, can be significant. Using tiered storage can save you significant money by moving less frequently accessed data to cheaper “cold” storage while keeping active files in “hot” storage.
FinOps (Finance + Operations) has become essential for managing cloud costs. It involves applying financial discipline to cloud spending through regular reviews, budgets, and alerts. We help clients implement cost optimization strategies to ensure they get the best value from their cloud investment. Find proven strategies for cloud cost optimization.
Common challenges with cloud based data storage
While powerful, cloud based data storage has potential challenges to consider:
- Latency: Accessing data over the internet can introduce delays, which may affect time-sensitive applications.
- Vendor lock-in: Deep integration with one provider’s services can make it difficult and costly to switch later.
- Internet dependency: No internet means no access to your primary cloud data, requiring backup plans and offline sync capabilities.
- Potential outages: Even major providers experience rare outages that can disrupt business. Contingency plans are key.
- Security risks: The shared responsibility model means misconfigurations on your end can create vulnerabilities.
Understanding these challenges is the first step to addressing them. With proper planning, they become manageable risks. Learn more about common cloud security challenges and practical solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cloud Storage
We love helping our clients understand cloud based data storage better. Over the years, we’ve noticed the same questions come up again and again in our conversations with business owners across Michigan. Here are the answers to the most common ones we hear.
Is cloud storage secure for my business?
Yes, cloud based data storage is often more secure than on-premise solutions. Major providers invest billions in security measures that most businesses cannot afford. However, security is a shared responsibility. The provider secures the physical infrastructure, while you are responsible for securing your data on the cloud.
Your responsibilities include using encryption, managing access controls to limit who can see what, and configuring services correctly to prevent data exposure. We help you manage your side of this responsibility to ensure your data is protected. Our cloud security monitoring solutions can help you keep an eye on everything.
How much does cloud storage typically cost?
Cloud storage pricing is typically a pay-per-use model, similar to a utility bill. Costs are influenced by several factors:
- Storage capacity: The amount of data you store.
- Storage tiers: Frequently accessed (“hot”) data costs more than archived (“cold”) data.
- Data transfer fees: Uploading data is often free, but downloading (egress) large amounts can incur costs.
- Requests: Each action, like accessing or modifying a file, has a small associated cost.
This model allows costs to scale with your business needs. We help clients understand and optimize these costs to ensure they are reasonable. Learn more about effective cloud computing cost management strategies.
Can I access my files if I’m offline?
Yes, most cloud storage services offer offline access features. Through file syncing, copies of selected files or folders are downloaded to your local device (computer, phone, or tablet). You can open, edit, and save these local copies without an internet connection.
Any changes you make are automatically uploaded to the cloud once you reconnect. This allows you to remain productive even when offline. You can typically control which files are available offline in your device’s settings, but you won’t have access to your entire cloud repository, only the synced files.
Conclusion: Securing Your Data’s Future in the Cloud
Moving to cloud based data storage is more than a technological shift; it’s a fundamental change in how businesses operate and compete. The explosive market growth confirms that this is the new reality for modern business operations.
Cloud storage offers the ability to scale without limits, collaborate without boundaries, and protect data with enterprise-grade security. It allows you to shift from capital expenses to predictable operational costs, investing resources in growth instead of server maintenance. With automatic backups and disaster recovery, your data is protected from threats like ransomware and hardware failure, while global accessibility keeps your team productive from anywhere.
While there are considerations like choosing the right deployment model and managing costs, these challenges are manageable with expert guidance. At Kraft Business Systems, we’ve helped businesses across Michigan make smart technology choices for years. We understand that every business has unique needs, from a small shop in Traverse City to a growing company in Detroit.
We partner with you to design a cloud based data storage strategy that grows with your business and supports your long-term goals. The future belongs to businesses that can adapt, collaborate, and protect their data intelligently. Cloud storage is key to positioning your business for success.
Ready to explore how cloud based data storage can transform your operations? We can help you steer this transition. Learn more about our document management system services and how we can assist your business.