AI Overview:
This guide delivers a clear, actionable cybersecurity roadmap for small businesses—especially Michigan organizations in regulated industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and education. It outlines a practical 10-point checklist covering identity protection (MFA, strong passwords), human risk reduction (employee training), technical controls (endpoint security, firewalls, encryption, patching), resilience (backups, disaster recovery), and preparedness (incident response, access monitoring). The key takeaway: cybersecurity isn’t a single tool but a layered, proactive strategy that reduces risk, ensures compliance, protects data, and strengthens long-term business resilience.
Protecting your small business from digital threats is more critical than ever. A single cyberattack can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive customer and company data, and permanently erode the trust you have worked hard to build. For Michigan-based businesses in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and education, the stakes are significantly higher due to specific compliance requirements and the immense value of the data you handle daily. Failing to secure your digital assets is not just a technology issue; it is a direct threat to your company’s financial stability and future.
This guide provides a prioritized, actionable collection of the most effective cybersecurity tips for small businesses. We will move beyond generic advice to offer specific, practical strategies that you can implement immediately to strengthen your organization’s security posture. You will find clear instructions on a range of essential protections, from quick wins like enforcing robust password policies to more comprehensive initiatives like establishing a formal disaster recovery plan.
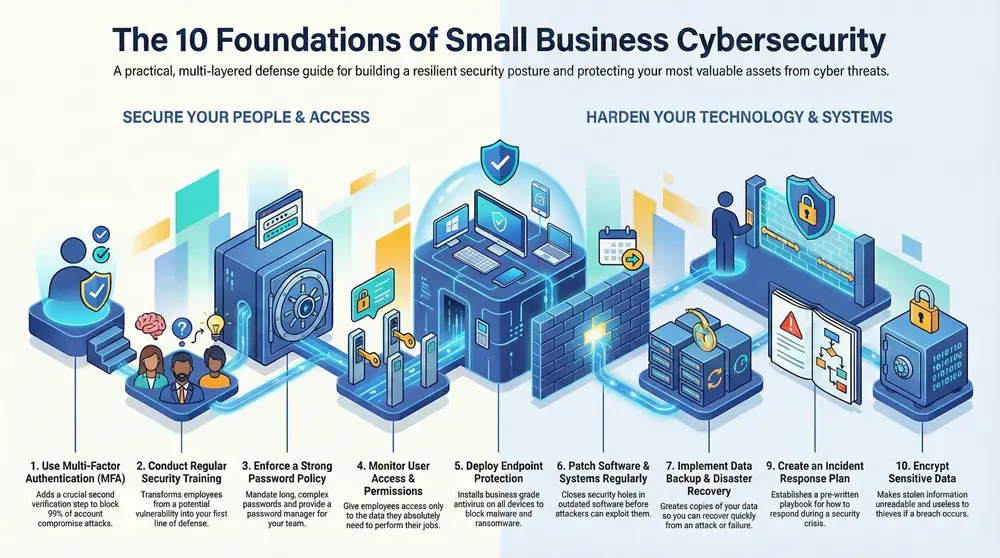
We will cover ten foundational areas critical for building a resilient defense. These include:
- Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Conducting regular employee security training
- Deploying advanced endpoint and antivirus solutions
- Establishing a strong password policy
- Executing timely software and system patching
- Creating a data backup and disaster recovery strategy
- Configuring a firewall with network segmentation
- Developing a formal incident response plan
- Monitoring user access and permissions
- Using encryption to protect sensitive data
Consider these ten items your essential checklist for creating a secure operational environment. Each tip is designed to be a concrete step toward safeguarding your business, ensuring you are prepared to face modern digital challenges head-on.
1. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone are no longer sufficient to protect your business’s critical data. A single compromised password can give a threat actor complete access to your systems. This is why implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is one of the most effective cybersecurity tips for small businesses. MFA adds a crucial verification step, requiring users to prove their identity with more than just a password.
This method combines something you know (your password) with something you have (like a code from an authenticator app on your phone) or something you are (a fingerprint or face scan). Even if a cybercriminal steals an employee’s password, they cannot access the account without the second factor, effectively stopping the attack.
How to Implement MFA Effectively
For Michigan businesses, this isn’t a complex, enterprise-level project. Start by securing your most vulnerable and valuable assets. E-commerce platforms like Shopify now enforce MFA for administrative accounts, and many small law firms leverage the built-in MFA features of Google Workspace or Microsoft 365 to protect client-attorney communications. These systems make rolling out MFA straightforward. A phased approach is key to managing this change successfully.
To get started, consider these actionable steps:
- Prioritize Critical Systems: Begin by enabling MFA on email accounts, financial software, and any system containing sensitive customer or company data.
- Choose Authenticator Apps: Encourage the use of authenticator apps (like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator) over SMS-based codes, which can be vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks.
- Train Your Team: Provide clear, simple instructions and training sessions to ensure every employee understands why MFA is important and how to use it.
- Enforce Company-Wide: Make MFA mandatory for all users, including executives and IT staff. Inconsistent application creates security gaps that attackers can exploit.
- Secure Recovery Codes: Instruct users to generate backup recovery codes and store them in a secure, offline location.
Adopting MFA is a foundational component of modern identity and access management. It drastically reduces the risk of unauthorized access, protecting your business from data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. By taking this single step, you significantly strengthen your overall security posture.
2. Conduct Regular Employee Security Training
Your technology can be secure, but a single click by an untrained employee can bypass all of it. Cybercriminals frequently target people, not systems, using phishing and social engineering because it’s often the easiest way in. This is why ongoing security awareness training is one of the most vital cybersecurity tips for small businesses, transforming your staff from a potential vulnerability into your first line of defense.
Effective training educates employees about current threats, teaches them how to recognize malicious attempts, and clarifies their role in protecting company data. Studies consistently show that a well-informed workforce dramatically reduces the likelihood of a successful cyberattack, delivering one of the highest returns on investment of any security measure. It’s about building a vigilant, security-first mindset.
How to Implement Security Training Effectively
This doesn’t require a full-time training department. Many Michigan businesses see great success using platforms like KnowBe4 to reduce phishing susceptibility, while local healthcare clinics use SANS training to meet HIPAA compliance requirements. The goal is to make security a continuous conversation, not a one-time event. For a deeper look into this approach, learn more about creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
To get started, consider these actionable steps:
- Establish a Regular Cadence: Conduct formal training sessions at least quarterly and supplement them with monthly or weekly security reminders.
- Use Interactive Learning: Move beyond static presentations. Use engaging, scenario-based modules and real-world examples to make the lessons stick.
- Test and Measure: Regularly send simulated phishing emails to test employee awareness. Use the results to identify knowledge gaps and provide targeted follow-up training.
- Make it Role-Specific: Customize training to be relevant to an employee’s role. An accountant needs different guidance on wire fraud than a salesperson does on protecting customer data.
- Reinforce Positive Behavior: Acknowledge and celebrate employees who correctly report phishing attempts or demonstrate strong security practices.
By investing in your people, you create a powerful human firewall. This proactive approach to risk management is crucial for defending against the most common entry points for cyberattacks and protecting your business’s sensitive information and reputation.
3. Deploy Endpoint Protection and Antivirus Solutions
Every device connected to your network, from a desktop computer to a company smartphone, is an “endpoint” and a potential entry point for attackers. Relying solely on a network firewall is insufficient, as malware can easily bypass it through an infected email attachment or a malicious download. Deploying endpoint protection and antivirus solutions provides essential, device-level security to prevent infections before they can spread across your network.
Modern endpoint protection goes far beyond traditional antivirus. It combines anti-malware, firewall controls, and advanced behavioral analysis to detect and block threats in real-time. This comprehensive approach is one of the most crucial cybersecurity tips for small businesses, as it directly addresses a primary attack vector used by cybercriminals.
How to Implement Endpoint Protection Effectively
For small businesses in Michigan, this is a foundational security measure. Many dental offices are successfully implementing solutions like Bitdefender to protect patient health information, while local manufacturing firms might use Microsoft Defender for Business to secure both office workstations and production floor terminals. These tools provide centralized management and visibility, making them easy to deploy and monitor.
To get started, consider these actionable steps:
- Choose a Business-Grade Solution: Select a platform designed for business use (like CrowdStrike, Microsoft Defender, or Bitdefender) over free, consumer-grade antivirus. Business solutions offer central management, reporting, and more robust protection features.
- Enable Automatic Updates and Scans: Ensure the software is configured to update its threat definitions automatically and run regular, scheduled scans on all devices. Outdated software is a significant security risk.
- Use Cloud-Based Management: Cloud-managed solutions simplify administration, allowing your IT team or provider to monitor all endpoints from a single dashboard without needing physical access to each device.
- Combine with DNS Filtering: Enhance your protection by adding DNS filtering, which blocks access to known malicious websites at the network level, preventing users from ever reaching them.
- Monitor and Respond to Alerts: Actively monitor alerts from your endpoint protection platform. A prompt response can contain a threat before it escalates into a full-blown data breach.
Proper endpoint security acts as your last line of defense against malware. By protecting each individual device, you significantly reduce the risk of a single compromised computer leading to a catastrophic network-wide incident. To understand more about the specific threats these tools defend against, you can learn more about safeguarding your business from Trojan malware.
4. Establish a Strong Password Policy
Relying on weak or reused passwords is like leaving your business’s front door unlocked. A single compromised credential can provide a direct path for attackers into your network, leading to data theft, financial fraud, and significant operational disruption. Establishing a formal, enforced password policy is a foundational security measure that moves your business from relying on hope to enforcing a standard of protection.
A strong password policy is a set of rules that governs how passwords are created, used, and managed across your entire organization. This policy removes guesswork and ensures every employee, from the front desk to the CEO, adheres to the same high security standards. It is one of the most cost-effective cybersecurity tips for small businesses to implement immediately.
How to Implement a Strong Password Policy
For Michigan businesses, this doesn’t require complex software. It starts with clear communication and leveraging tools you may already have. A tech startup in Ann Arbor can use a password manager like Dashlane or Bitwarden to generate and store complex credentials, while a small financial firm in Grand Rapids might enforce 16-character password requirements through their Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace settings.
To create an effective policy, consider these actionable steps:
- Set Strong Requirements: Mandate a minimum length of 12-14 characters. Enforce complexity by requiring a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Deploy a Password Manager: Provide a business password manager like 1Password or LastPass. This helps employees create, store, and share unique, complex passwords securely without needing to memorize them.
- Prohibit Password Reuse: Your policy must explicitly forbid using the same or similar passwords across different internal and external services.
- Train on Passphrase Creation: Teach employees to create memorable yet strong passphrases, such as “Correct!Horse*Battery8Staple”, which are easier to remember than random strings of characters.
- Monitor for Breached Credentials: Use tools that can check if company email addresses and passwords have appeared in public data breaches, and force a password reset if a compromise is found.
Implementing a robust password policy is a critical component of your identity and access management strategy. By setting clear standards and providing the right tools, you dramatically reduce the risk of credential-based attacks, protecting your business’s sensitive data and reputation.
5. Regular Software and System Patching
Failing to update software is like leaving your business’s front door unlocked. Cybercriminals actively scan for systems with outdated software, as these unpatched vulnerabilities are among the most common and easily exploited entry points. Regular software and system patching involves applying updates released by vendors to fix security flaws and bugs, effectively closing these digital doors before an attacker can walk through.
This proactive maintenance is a cornerstone of effective cybersecurity. When a vulnerability is discovered, vendors like Microsoft release a “patch.” Attackers then reverse-engineer these patches to understand the flaw and create tools to exploit it on any system that has not yet been updated. A consistent patching schedule ensures you stay ahead of these threats.
How to Implement Patching Effectively
Managing updates doesn’t have to be an overwhelming manual process. For Michigan-based manufacturers, using tools like Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) can centralize and automate patching for all Windows machines on the factory floor. Similarly, many non-profits can schedule monthly updates for their Linux servers to maintain security without disrupting daily operations. The key is to create a structured, repeatable process.
To build a strong patch management program, consider these steps:
- Maintain an Inventory: You can’t protect what you don’t know you have. Keep an up-to-date inventory of all software, operating systems, and their versions.
- Automate Where Possible: Enable automatic updates for endpoint devices like laptops and desktops and for non-critical software to ensure they are consistently patched.
- Schedule Critical Updates: For servers and essential business systems, schedule patching during planned maintenance windows to minimize operational disruption.
- Test Before Deploying: Whenever feasible, test critical patches on a non-production system first to ensure they don’t cause conflicts with other business applications.
- Establish Rollback Plans: Have a clear procedure in place to revert a patch if it causes unexpected issues, ensuring business continuity.
A disciplined approach to patching is one of the most cost-effective cybersecurity tips for small businesses. It directly mitigates a huge percentage of common threats, from ransomware to data exfiltration, by hardening your systems against known attack vectors.
6. Implement Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
A single catastrophic event, such as a ransomware attack, hardware failure, or natural disaster, can wipe out your business’s critical data, grinding operations to a halt. Implementing a robust data backup and disaster recovery plan is not just an IT task; it is a fundamental business continuity strategy. This process involves creating copies of your data and having a documented plan to restore it quickly after an incident, ensuring you can recover with minimal downtime and financial loss.
The industry standard is the 3-2-1 backup rule: maintain at least three copies of your data, on two different types of storage media, with one copy located offsite. For small businesses, modern cloud-based solutions have made this approach both affordable and easy to manage, providing reliable protection without requiring complex on-premises infrastructure. This is a critical cybersecurity tip for small businesses that protects against both accidental and malicious data loss.
How to Implement Data Backup and Recovery Effectively
Michigan businesses can leverage user-friendly, automated platforms to secure their data. For instance, a dental office in Grand Rapids might use a service like Backblaze for automated daily backups of patient records and imaging files, while a law firm in Detroit could implement an Acronis solution to protect sensitive client case files. The goal is to make the backup process automatic, consistent, and reliable, removing the risk of human error.
To create a resilient backup strategy, follow these steps:
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Strictly adhere to the principle of three copies, two media types, and one offsite location. This provides redundancy against multiple failure scenarios.
- Test Your Restore Process: A backup is useless if it cannot be restored. Regularly test your recovery procedures at least quarterly to verify data integrity and confirm you can meet your recovery time objectives.
- Encrypt All Backups: Ensure backups are encrypted both while being transferred (in transit) and while stored (at rest). This protects your data even if the backup media is stolen or compromised.
- Use Immutable Backups: To combat ransomware, use immutable or air-gapped backups. These are read-only copies that cannot be altered or deleted by attackers, guaranteeing a clean version of your data for recovery.
- Document Everything: Create a clear disaster recovery plan that documents procedures, responsible personnel, and expected timelines for restoring critical systems.
A well-planned data backup and disaster recovery strategy is your ultimate safety net. It ensures that no matter what disruption occurs, from a simple server failure to a sophisticated cyberattack, your business can get back on its feet and continue serving its customers.
7. Set Up a Firewall and Network Segmentation
A firewall is the digital gatekeeper for your business network, acting as the first line of defense against cyber threats. It monitors all incoming and outgoing network traffic, deciding what to allow or block based on a predefined set of security rules. Pairing a firewall with network segmentation takes this protection a step further by dividing your network into smaller, isolated sub-networks.
This strategy prevents attackers from moving freely across your entire network if one area is breached. For example, if your guest Wi-Fi is compromised, the threat is contained and cannot access your critical servers or financial systems. This containment significantly reduces the potential damage of a security incident.
How to Implement Firewalls and Segmentation
This is a core networking security practice applicable to any Michigan business, from a small manufacturing firm using a Fortinet FortiGate to protect its shop floor network to a nonprofit deploying a Ubiquiti UniFi security gateway. The goal is to create barriers that limit access and contain threats. A modern firewall can inspect traffic content, not just its source and destination, providing much deeper protection.
To effectively deploy this crucial cybersecurity tip for small businesses, consider these steps:
- Segment by Function: Create separate network zones for different purposes. Common segments include a guest network, an internal employee network, a server network for critical data, and a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) for public-facing services like your website.
- Implement Zero-Trust Principles: Configure firewall rules with a “deny-all” default. This means no traffic is allowed between segments unless you create a specific rule to permit it. This enforces the principle of least privilege.
- Enable Advanced Security Features: Use modern firewalls that offer Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS). These features can identify and block sophisticated threats hidden within legitimate-looking traffic.
- Review Rules Regularly: Your business changes, and so should your firewall rules. Review and update them at least quarterly to remove outdated rules and ensure they align with your current operational needs.
- Log and Monitor Traffic: Actively log firewall activity and monitor it for unusual patterns. These logs are invaluable for identifying a potential attack in progress and for forensic analysis after an incident.
Implementing a properly configured firewall and segmenting your network are fundamental steps in network security. This layered defense limits an attacker’s mobility and protects your most valuable assets from unauthorized access, making your business a much harder target.
8. Establish an Incident Response Plan
When a security incident occurs, panic and confusion can lead to costly mistakes. An Incident Response (IR) Plan is your pre-written playbook for how to detect, contain, and recover from a cybersecurity event. It provides a structured guide that removes guesswork during a high-stress situation, ensuring a coordinated and effective response. For a small business, this plan is the difference between a manageable event and a catastrophic failure.
This document designates roles, outlines communication protocols, and provides step-by-step actions for different incident types, from a minor data leak to a full-blown ransomware attack. A well-defined plan dramatically reduces damage, minimizes downtime, and helps you meet legal and regulatory notification requirements, protecting both your operations and your reputation.
How to Create an Effective IR Plan
You don’t need to start from scratch. Proven frameworks from organizations like the SANS Institute and NIST provide excellent templates. For example, a Michigan-based healthcare clinic can adapt HHS breach notification procedures into its plan, while a local retail business might use a simplified SANS template to guide its response to a point-of-sale system compromise. The goal is to create a clear, actionable document before you need it.
To build your plan, consider these critical steps:
- Define Roles and Responsibilities: Assign a clear “incident commander” and outline the specific duties of each team member during a crisis.
- Create Incident Playbooks: Develop simple, step-by-step checklists for common scenarios like ransomware, business email compromise, and data breaches.
- Establish Communication Protocols: Document how you will communicate internally with staff and externally with customers, law enforcement, and regulatory bodies. Include pre-drafted message templates.
- Maintain Key Contacts: Keep a list of external contacts, including your IT provider, legal counsel, and a cybersecurity forensics firm, in an accessible location (including an offline copy).
- Practice and Refine: Conduct quarterly tabletop exercises where you walk through a simulated incident. This helps identify gaps in your plan and familiarizes your team with their roles.
Developing a robust IR plan is a core component of risk management. It prepares your business to act decisively, turning a potential disaster into a controlled, survivable event. This proactive measure is one of the most vital cybersecurity tips for small businesses, ensuring resilience in the face of an attack.
9. Monitor and Audit User Access and Permissions
Giving every employee the “keys to the kingdom” is a significant security risk. A foundational cybersecurity tip for small businesses is to ensure employees only have access to the data and systems they absolutely need to perform their jobs. This is known as the Principle of Least Privilege, and it drastically reduces your attack surface and limits the potential damage from a compromised account.
Controlling user access is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing monitoring and regular audits. By logging and reviewing who accesses what and when, you can detect unauthorized or suspicious activity. This process is critical for preventing both insider threats and external attacks, ensuring that access rights remain appropriate as roles and responsibilities change within your organization.
How to Implement Access Control Effectively
Many businesses can start by leveraging the built-in tools within their existing platforms. For example, government contractors in Michigan often implement stringent access controls using Microsoft Azure AD to meet compliance requirements, while healthcare providers may use identity management platforms like Okta to secure patient data. The goal is to create a structured system for granting and revoking access.
To get started, consider these actionable steps:
- Implement the Principle of Least Privilege: When creating a new user account, start with zero access and only add the specific permissions required for that person’s role.
- Conduct Quarterly Access Reviews: At least once per quarter, review every user’s access rights to ensure they are still necessary. Involve department managers in this process.
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Instead of assigning permissions one-by-one, create roles (e.g., “Accountant,” “Sales Rep”) with pre-defined access levels. This simplifies management and reduces errors.
- Disable Unused Accounts Promptly: Immediately deactivate the accounts of former employees or contractors to prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitor Privileged Accounts: Pay close attention to accounts with administrative rights, as they are high-value targets for attackers. Log and audit all their activities.
Properly managing access is fundamental to a strong security posture. To ensure proper control over who accesses your business’s sensitive data, refer to a complete security access guide for user roles and permissions. By systematically managing and auditing user permissions, you protect your critical assets and build a more resilient defense against cyber threats.
10. Use Encryption for Data Protection
In its simplest form, encryption is the process of converting readable data into a coded format that can only be unlocked with a specific key. This cryptographic shield makes your sensitive information unintelligible to anyone without authorized access. For a small business, encryption is a non-negotiable layer of defense that protects data both when it is being sent over a network (in transit) and when it is stored on a device (at rest).
Even if a physical device like a laptop is stolen or a server is breached, encryption ensures the stolen data remains useless to the thief. This technology is a core requirement for many compliance frameworks, including HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA, making it an essential practice for businesses handling personal or sensitive information.
How to Implement Encryption Effectively
Implementing encryption doesn’t require a massive budget or specialized team. Many tools you already use have powerful, built-in encryption features. For example, a Michigan-based e-commerce shop can secure customer transactions by activating a free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt, while a small financial advisory firm can use Microsoft BitLocker to encrypt the entire hard drive of every company laptop, protecting client data from physical theft.
Consider these practical steps to get started:
- Enable Full-Disk Encryption: Activate BitLocker (on Windows) or FileVault (on macOS) on all company laptops, desktops, and servers. This protects all data stored on the device if it’s lost or stolen.
- Secure Your Website with HTTPS: Install an SSL/TLS certificate on your website to encrypt data exchanged between your visitors and your server. This is critical for any site that collects user information.
- Encrypt Email Communications: Use services like Virtru or ProtonMail for sending emails containing sensitive information, ensuring only the intended recipient can read the message.
- Use Encrypted Backups: Ensure that your backup solution encrypts the data it stores, both in the cloud and on local devices.
- Manage Data Destruction: Remember that encryption protects data on active devices. When hardware is decommissioned, physical destruction is necessary. Understanding processes like secure hard drive shredding is critical for a complete data lifecycle security strategy.
Encryption is a foundational element of a robust security program. By making your data unreadable to unauthorized parties, you create a powerful barrier against data breaches, significantly reducing the potential for financial loss and regulatory penalties. It’s one of the most effective cybersecurity tips for small businesses looking to protect their digital assets.
10-Point Small Business Cybersecurity Comparison
| Control | Implementation complexity | Resource requirements | Expected outcomes | Ideal use cases | Key advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Low–Medium | Authenticator apps/hardware, admin setup, user support | Significant reduction in account compromise | Admin accounts, remote/cloud access | Blocks credential-based attacks; broad platform support |
| Conduct Regular Employee Security Training | Low | Training platform, instructor time, phishing simulation tools | Lower phishing click rates; stronger security culture | All staff, high-email roles | High ROI; reduces human-targeted risk |
| Deploy Endpoint Protection and Antivirus Solutions | Medium | Endpoint agents, management console, subscriptions | Prevents/matches common malware and ransomware attempts | All endpoints (PCs, laptops, mobile) | Centralized detection and automated response |
| Establish a Strong Password Policy | Low | Policy enforcement, password managers | Fewer brute-force successes; compliance alignment | All user and service accounts | Simple to implement; supports stronger authentication |
| Regular Software and System Patching | Medium–High | Patch management tools, testing environments, maintenance windows | Closes known vulnerabilities; reduces exploit exposure | Servers, workstations, applications | Prevents many attacks; improves stability |
| Implement Data Backup and Disaster Recovery | Medium | Backup storage (cloud/offsite), DR plans, testing resources | Faster recovery from ransomware/data loss; business continuity | Critical data stores, POS, customer records | Enables restore and continuity; immutable options available |
| Set Up a Firewall and Network Segmentation | Medium–High | Firewalls/NGFW, VLANs, network expertise | Restricted access; limited lateral movement on compromise | Guest vs internal networks, sensitive servers | Network-level containment and visibility |
| Establish an Incident Response Plan | Medium | IR playbooks, designated roles, external contacts for forensics/legal | Faster containment and recovery; clear communication | Breach/ransomware/outage scenarios | Reduces damage; standardized response under pressure |
| Monitor and Audit User Access and Permissions | Medium–High | IAM/PAM tools, logging/storage, admin effort | Reduced insider risk; traceable access changes | Privileged users, regulated environments | Enforces least privilege; provides audit trails |
| Use Encryption for Data Protection | Medium | TLS certs, KMS/HSM, key management processes | Data unreadable if exfiltrated; regulatory compliance | Databases, backups, web/email, endpoints | Protects confidentiality; meets compliance standards |
Securing Your Business for What’s Next
Navigating the complexities of digital security can feel like a monumental task, but the journey to a more secure business begins with clear, decisive action. The cybersecurity tips for small businesses we’ve outlined are not just a checklist; they represent a fundamental shift in how you protect your organization’s most valuable assets. By moving beyond reactive fixes to proactive defense, you build a resilient foundation that can withstand the constantly evolving tactics of cyber adversaries.
The ten strategies detailed in this guide, from implementing multi-factor authentication to establishing a formal incident response plan, work together to create a multi-layered security posture. No single solution is a silver bullet. A strong password policy is crucial, but its effectiveness is magnified exponentially when combined with MFA. Similarly, robust data backups provide a vital safety net, but they are most powerful when supported by endpoint protection and network firewalls that prevent an incident in the first place.
From Knowledge to Action: Your Immediate Next Steps
The true value of this information lies in its application. Reading these tips is the first step, but implementation is what separates vulnerable businesses from secure ones. Your immediate goal should be to translate this knowledge into tangible action. Start by performing a quick, internal audit based on the areas we’ve covered.
- Identify Your Biggest Gaps: Which of the ten tips represents your most significant vulnerability right now? Is it a lack of formal employee training or an inconsistent patching schedule? Pinpoint the area of greatest risk.
- Prioritize a “Quick Win”: Select one or two high-impact, low-effort changes you can make this week. Enforcing MFA across key applications or updating your password policy are excellent starting points that deliver immediate security benefits.
- Schedule a Deeper Review: Block time on your calendar to systematically review each of the ten points. Create a simple project plan outlining who is responsible for each area, what resources are needed, and a realistic timeline for implementation.
The Lasting Impact of a Proactive Security Culture
Ultimately, these cybersecurity tips for small businesses are about more than just technology; they are about building a culture of security. When every employee, from the front desk to the executive suite, understands their role in protecting company data, your human firewall becomes your strongest asset. Consistent training, clear policies, and leading by example transform security from an IT department problem into a shared organizational responsibility.
This proactive approach does more than prevent data breaches and financial loss. It builds trust with your clients, partners, and employees. For businesses in Michigan, especially those in regulated sectors like healthcare, government, or education, demonstrating a commitment to robust cybersecurity is a powerful competitive differentiator. It signals reliability, professionalism, and a dedication to protecting the sensitive information entrusted to you. While the path to comprehensive security is an ongoing commitment, the steps you take today are a direct investment in your company’s future stability, reputation, and success. Protecting your business is not just about defending against what’s happening now, but preparing for what comes next.
Ready to move from planning to implementation with an expert partner? The team at Kraft Business Systems specializes in delivering comprehensive, managed cybersecurity solutions tailored to the unique needs of Michigan businesses, helping you implement these critical protections and more. Visit Kraft Business Systems to schedule a consultation and fortify your defenses today.